Autonomous Threat Sweeper
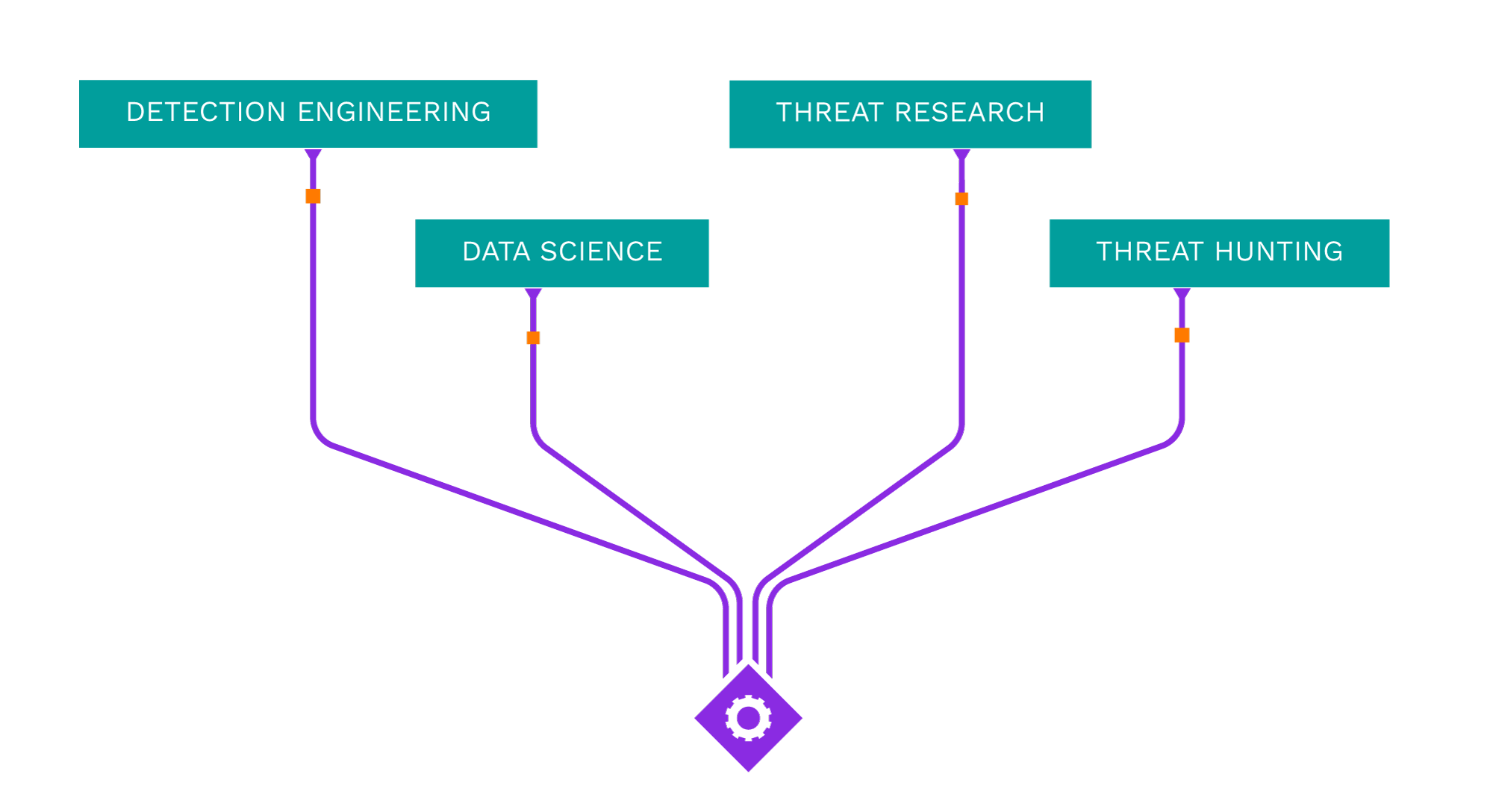
Acting as your own dedicated Cyber Rapid Response Team, Securonix Autonomous Threat Sweeper (ATS) automatically and retroactively hunts for new and emerging threats based on the latest threat intelligence from our Threat Labs Team.
Latest ATS Entries
All indicators of compromise (IOC) and Spotter queries are available on our GitHub repository.
—
- Intel Source:
- SOC Radar
- Intel Name:
- Security_Risks_in_OpenMetadata
- Date of Scan:
- 2024-04-19
- Impact:
- LOW
- Summary:
- Researchers from Microsoft have discovered the critical vulnerabilities within the OpenMetadata platform, an open-source system designed to manage metadata across various data sources. These vulnerabilities affect versions of OpenMetadata earlier than 1.3.1, potentially allowing attackers to bypass authentication and execute Remote Code Execution (RCE).
Source:
https://socradar.io/openmetadata-attackers-cryptomine-in-kubernetes/
—
- Intel Source:
- NSFOCUS
- Intel Name:
- Palo_Alto_Networks_Fixes_Critical_Command_Injection_Vulnerability_in_PAN_OS_Firewall
- Date of Scan:
- 2024-04-19
- Impact:
- LOW
- Summary:
- NSFOCUS CERT has detected a critical command injection vulnerability (CVE-2024-3400) in Palo Alto Networks’ PAN-OS firewall operating system. Unauthenticated attackers could exploit this flaw to execute arbitrary code with root privileges on affected firewalls. Palo Alto Networks has released security updates addressing this vulnerability, with the PoC already public and actively exploited. The CVSS score of 10.0 underscores the severity of the issue. Users are urged to upgrade to patched versions immediately.
Source:
https://nsfocusglobal.com/palo-alto-networks-pan-os-command-injection-vulnerability-cve-2024-3400/
—
- Intel Source:
- Seqrite
- Intel Name:
- Unveiling_Ghost_Locker_2
- Date of Scan:
- 2024-04-19
- Impact:
- LOW
- Summary:
- Seqrite researchers have discovered the two versions of the Ghost Locker ransomware during their threat hunting activities. The initial variant, coded in Python, secures its presence by replicating itself in the Windows Startup directory and utilizes AES encryption to lock files. This variant communicates with a C2 server to dispatch ransom demands and extract data. The subsequent variant, mostly developed in Golang, mirrors the characteristics of the first iteration but distinguishes itself in terms of C2 server interactions and operational procedures. Moreover, it incorporates mechanisms to evade detection and carefully chooses files for encryption and data extraction.
—
- Intel Source:
- ASEC
- Intel Name:
- Analysis_of_Pupy_RAT
- Date of Scan:
- 2024-04-18
- Impact:
- LOW
- Summary:
- ASEC researchers discovered that many bad actors are using Pupy RAT, a tricky type of software. Pupy RAT allows them to control computers from far away and do things like stealing data and getting more control over the system. Now, it’s not just targeting Windows computers; it’s also affecting Linux systems, especially in countries like South Korea.
—
- Intel Source:
- Trend Micro
- Intel Name:
- UK_Law_Enforcement_Successfully_Takes_Down_Phishing_as_a_Service_Provider_LabHost
- Date of Scan:
- 2024-04-18
- Impact:
- MEDIUM
- Summary:
- UK’s Metropolitan Police Service, in collaboration with international law enforcement agencies and private industry partners, executed an operation leading to the takedown of the notorious Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) provider LabHost. LabHost, also known as LabRat, had gained notoriety since its emergence in late 2021 for offering a platform facilitating phishing attacks against numerous banks and organizations worldwide. With over 2,000 criminal users and more than 40,000 fraudulent sites deployed, LabHost posed a significant threat to global cybersecurity.
Source:
https://www.trendmicro.com/en_us/research/24/d/labhost-takedown.html
—
- Intel Source:
- CISA
- Intel Name:
- A_wide_range_of_Akira_ransomware
- Date of Scan:
- 2024-04-18
- Impact:
- HIGH
- Summary:
- According to a joint advisory from the FBI, CISA, Europol’s European Cybercrime Centre (EC3), and the Netherlands’ National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC-NL), the Akira ransomware operation has breached the networks of over 250 organizations and raked in roughly $42 million in ransom payments. Since March 2023, Akira ransomware has impacted a wide range of businesses and critical infrastructure entities in North America, Europe, and Australia. In April 2023, following an initial focus on Windows systems, Akira threat actors deployed a Linux variant targeting VMware ESXi virtual machines.
Source:
https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/cybersecurity-advisories/aa24-109a
—
- Intel Source:
- Thehackernews
- Intel Name:
- Malvertising_Campaign_Leveraging_Google_Ads_Distributes_MadMxShell_Backdoor
- Date of Scan:
- 2024-04-18
- Impact:
- MEDIUM
- Summary:
- Zscaler ThreatLabz researchers have uncovered a sophisticated malvertising campaign utilizing Google Ads to distribute a previously unknown backdoor named MadMxShell. The campaign involves the registration of multiple domains resembling legitimate IP scanner software, which are then promoted through Google Ads to target specific search keywords. Victims who visit these sites are tricked into downloading a malicious file disguised as IP scanner software. Once executed, the malware employs DLL side-loading and process hollowing techniques to infect systems, ultimately establishing a backdoor for gathering system information and performing malicious activities.
Source:
https://thehackernews.com/2024/04/malicious-google-ads-pushing-fake-ip.html
—
- Intel Source:
- Cisco Talos
- Intel Name:
- The_upload_of_confidential_documents_to_VirusTotal_by_OfflRouter_virus
- Date of Scan:
- 2024-04-18
- Impact:
- MEDIUM
- Summary:
- Recently, Cisco Talos discovered documents with some sensitive information from Ukraine. The documents had malicious VBA code, indicating they may be used as a trick to infect organizations. The virus, OfflRouter, has been known in Ukraine since 2015 and is still active on some Ukrainian organizations’ networks, based on over 100 original infected documents uploaded to VirusTotal from Ukraine and the documents’ upload dates.
—
- Intel Source:
- Zscaler
- Intel Name:
- The_newly_discovered_backdoor_MadMxShell
- Date of Scan:
- 2024-04-18
- Impact:
- LOW
- Summary:
- Zscaler provided the details of a new backdoor, MadMxShell, discovered by ThreatLabz. The backdoor is delivered through a ZIP archive and uses obfuscated shellcodes to extract and decode an executable file. It also has a dropper stage and a final backdoor stage for collecting system information and executing commands. The backdoor communicates with its C2 server through DNS MX queries and responses, using a custom method to encode data.
Source:
https://www.zscaler.com/blogs/security-research/malvertising-campaign-targeting-it-teams-madmxshell
—
- Intel Source:
- McAfee
- Intel Name:
- A_new_packed_variant_of_the_Redline_Stealer_trojan
- Date of Scan:
- 2024-04-18
- Impact:
- MEDIUM
- Summary:
- Recently, McAfee telemetry data showed the details of a new variant of the Redline Stealer trojan that uses Lua bytecode to perform malicious activities. It is prevalent in various regions and is distributed through GitHub. The trojan creates persistence on infected machines and communicates through HTTP, while also being able to take screenshots and steal data. McAfee also covered the analysis of the bytecode file and the techniques used by the threat actors, including creating a mutex and retrieving information from the Windows registry.
Source:
https://www.mcafee.com/blogs/other-blogs/mcafee-labs/redline-stealer-a-novel-approach/

Shared Security Content on Sigma
Securonix Threat Labs publishes up-to-date IOCs and threat hunting queries on Sigma, allowing you to tap into a vast community of collective defense and stay ahead of emerging threat research.
What's New from Threat Labs
-
BlogSecuronix Threat Research Knowledge Sharing Series: Detecting DLL Sideloading Techniques Found In Recent Real-world Malware Attack ChainsLearn More
-
BlogSecuronix Threat Research Security Advisory: Analysis of New DEEP#GOSU Attack Campaign Likely Associated with North Korean Kimsuky Targeting Victims with Stealthy MalwareLearn More
-
BlogSecuronix Threat Research Security Advisory: Analysis and Detection of STEADY#URSA Attack Campaign Targeting Ukraine Military Dropping New Covert SUBTLE-PAWS PowerShell BackdoorLearn More