Securonix Threat Labs
Get up-to-date threat content from the experts at Securonix Threat Labs.
Get up-to-date threat content from the experts at Securonix Threat Labs.
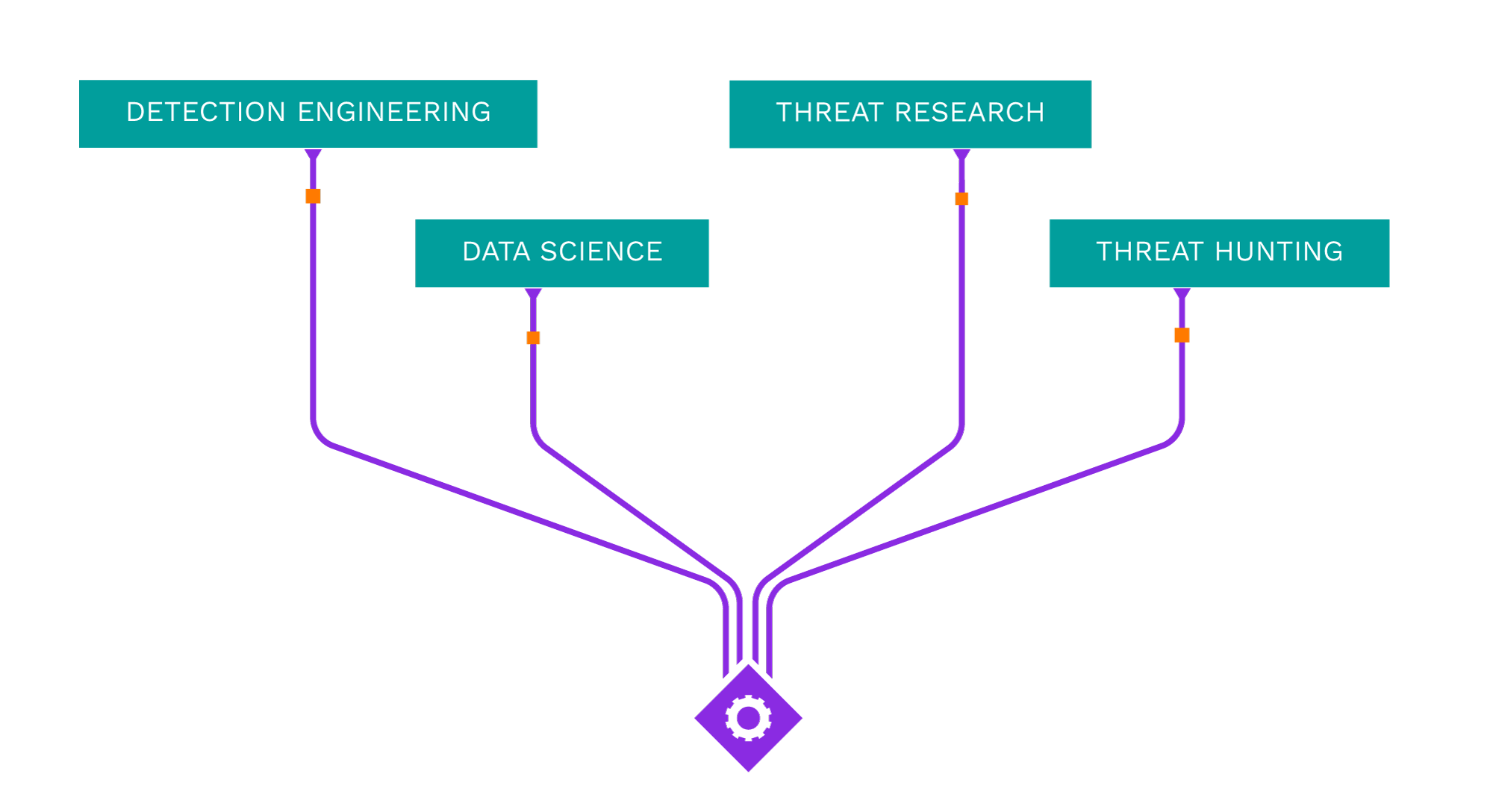
Securonix Threat Labs helps your team fend off rising threats by bringing the industry’s brightest minds together to equip you with the latest countermeasures and best practices.







Powered by Threat Labs
Acting as your own dedicated Cyber Rapid Response Team, Securonix Autonomous Threat Sweeper (ATS) automatically and retroactively hunts for new and emerging threats based on the latest threat intelligence from our Threat Labs Team.
All indicators of compromise (IOC) and Spotter queries are available on our GitHub repository.
Threat Content
Securonix Threat Labs publishes up-to-date IOCs and threat hunting queries on Sigma, allowing you to tap into a vast community of collective defense and stay ahead of emerging threat research.
Learn how Securonix is paving the way to make precise, and actionable security content a reality for our customers.