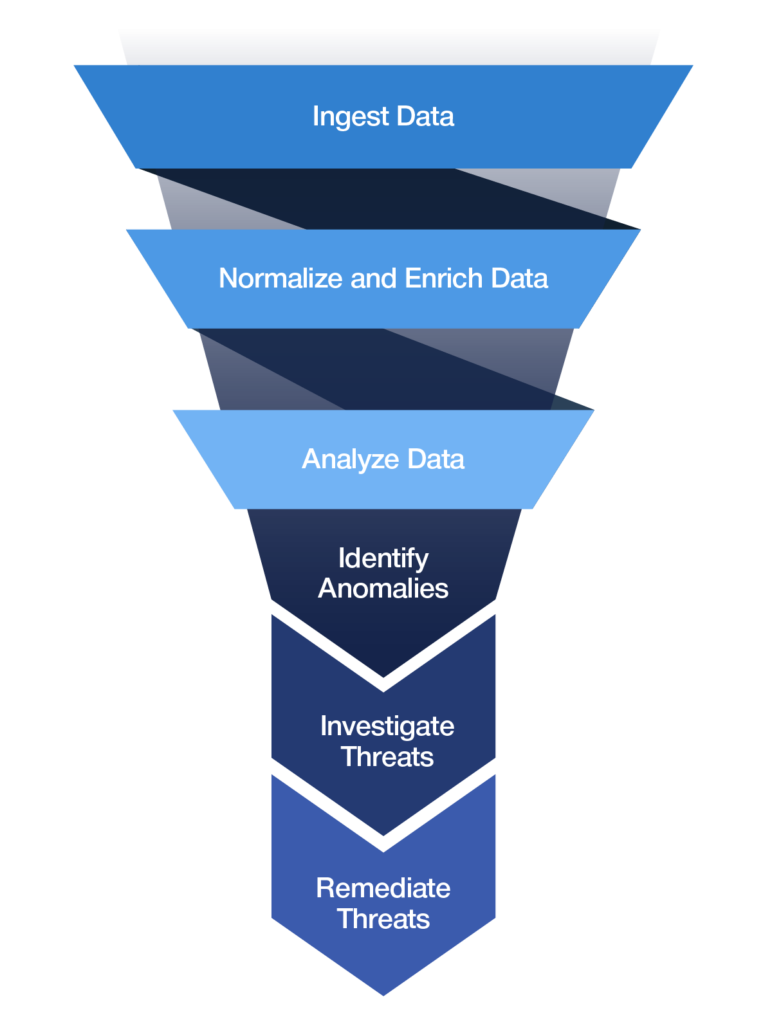
SIEM solutions use different techniques to draw usable conclusions from the data and find anomalies. These analytics techniques vary widely from vendor to vendor.
Legacy SIEMs rely on simple correlation and signature-based alerts. They are prone to error, produce a lot of noise in the form of false positives, and can only find known threats. This causes analysts to waste time chasing events that may or may not be credible threats.
A next-generation SIEM uses advanced analytic techniques, beyond signature-based approachs, to catch known and unknown threats. They use sophisticated machine learning algorithms to detect threats more accurately.
User and entity behavioral analytics (UEBA) is one type of advanced analytics that is integrated into next-generation SIEMs in order to provide better detection. Another technique used are threat chain models. These models help stitch together connected alerts in order to consolidate separate but related alerts into a threat sequence, increasing the risk score of the overall threat.